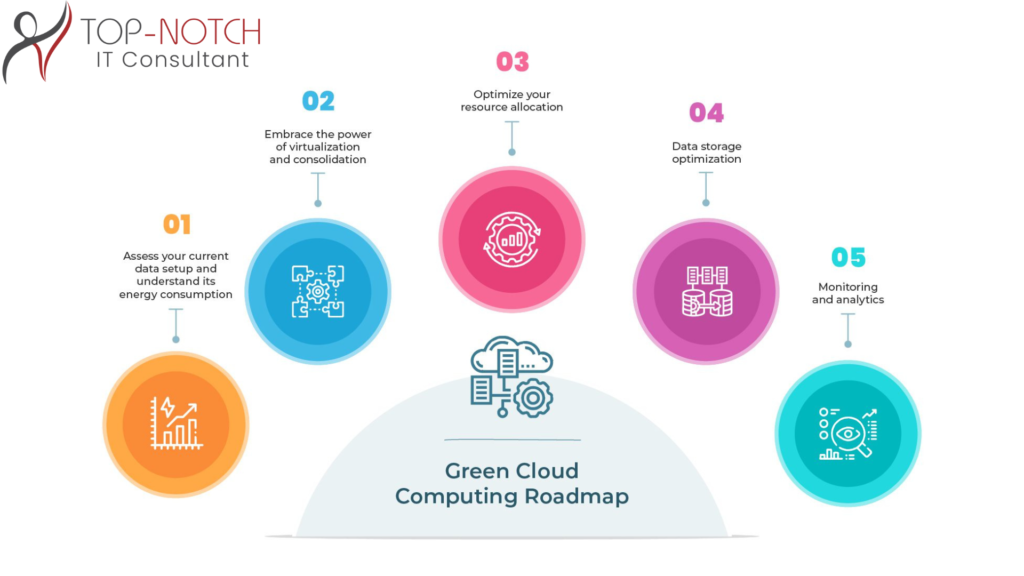
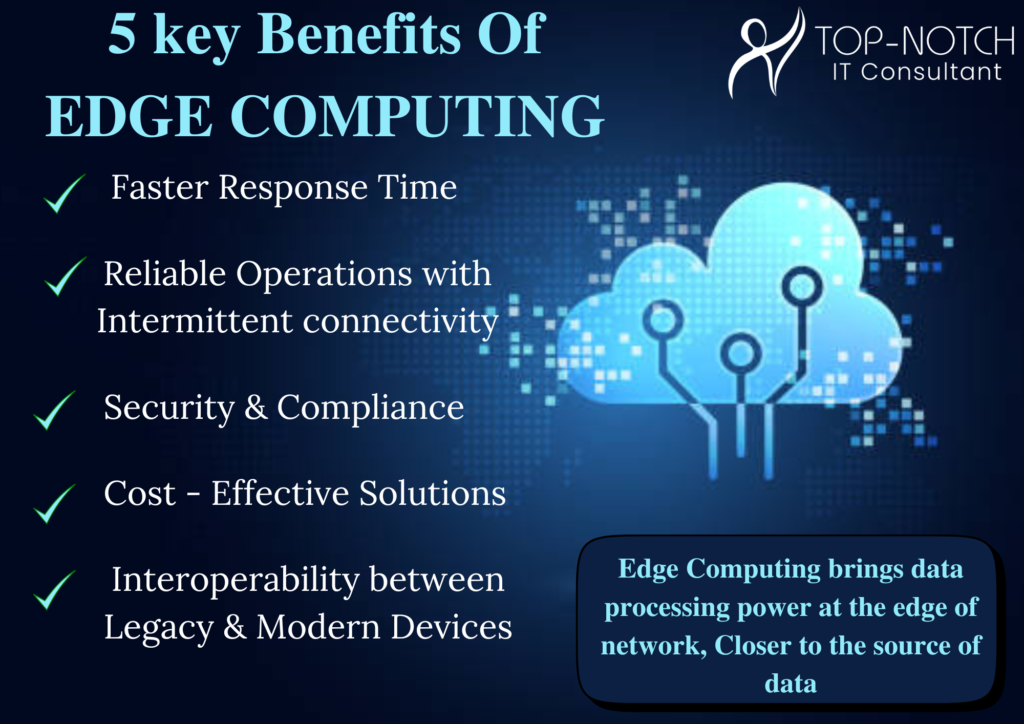
With the rapid advancement of digital technologies, it has resulted in enhanced complications in IT supply chains and data management. In an era, where the safety of data and transparency are important, blockchain technology is rising as one of the transformative solutions. Initially designed as a support system for cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, it has now found exclusive applications in various industries, which include IT supply chains and Data Integrity with blockchain. This centralized and immutable technology is giving a new shape to how organizations are managing supply chain management and safeguarding important data.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain is a well-distributed ledger technology or DLT that keeps a record of the transactions in various computers safely and transparently. Some of the important characteristics of blockchain are:
- Decentralization: Not similar to traditional databases which are under the control of a single entity, blockchain functions on a peer to peer network.
- Immutable: When recorded, blockchain data can’t be changed or deleted.
- Transparent: All transactions are visible to every participant present in the network, making sure there is good accountability.
- Safety: Blockchain makes use of cryptographic methods for the protection of data from getting exposed to any unauthorized access.
All these features make blockchain one of the best solutions for addressing difficulties in IT supply chains and the integration of data.

Role of blockchain in revolutionizing IT supply chains
Increased transparency and tracking
IT supply chains are complicated and involve several stakeholders, such as manufacturers, vendors, consumers and suppliers. In traditional supply chain systems it completely depends on centralized databases, which makes them highly vulnerable to ineffectiveness, no visibility and fraud. Blockchain makes sure there is end-to-end transparency that allows stakeholders to track products, verify their authenticity and do detection of anomalies in real time.
Example: Blockchain can assist IT companies in keeping track of raw materials that are being used in the making of chips and electronic components. Through the storage of supply chain data on a blockchain, it becomes easy for organizations to do verification of the ethical sourcing of materials and prohibit counterfeit products from making an entry into the market.
Enhanced effectiveness and reduction of cost
Blockchain removes the requirement for intermediaries and decreases manual paperwork through automation processes. These self-implementing contracts are programmed to execute actions automatically when all predefined conditions are met, lessening delays and the cost of operations.
Example: During IT procurements, smart contracts can help in the automation of purchase orders, and management of inventory and payments. This helps in the reduction of human intervention, and mitigation of errors and makes sure there are fast transactions, ultimately decreasing the cost of the supply chain.
Prevention of fraud and safety
Fraud in the supply chain is one of the substantial concerns in the IT sector, with forged components and unlawful changes that lead to severe security risks. Blockchain’s immutable ledger makes sure that all transactions are recorded permanently, making it impossible to manipulate data without ant detection thus providing Data protection in IT.
Example: Most IT firms are making use of the blockchain for the prevention of fraud in semiconductor supply chains by keeping track of the chips from production to deployment, making sure there is use of only genuine components.
Flexibility and management of risk
Disruptions such as cyberattacks, breaches in supply chains and global crises can have a high impact on the IT supply chains. The decentralized architecture of Blockchain increases resilience through the prevention of a single point of failure. As data is stored in various nodes, even when one node gets compromised, the whole system stays intact, decreasing the risk of cyber threats.
In addition, blockchain also allows proactive risk management offering real-time visibility into potential disruptions, facilitating IT firms in adapting and making some data-driven decisions swiftly.
Blockchain and data integrity management
Data integrity means accuracy, consistency and safety of data all through the lifecycle. In the IT sector, where cyber threats, data breaches and compliance needs pose difficulties, Blockchain is proving to be a game changer.
Immutable storage of data
The cryptographic mechanism of Blockchain makes sure that when data is recorded, it cannot be changed or tampered with. This is specifically useful when industries that need audit trails, safe record keeping and regulatory compliance.
Example: IT service providers make use of blockchain for maintaining logs of system updates, safety patches and software deployments. This makes sure there is compliance with the industry standards and prevention of unauthorized changes.
Safe management of identity
With increasing cyber threats, identity theft and breach of data are becoming one of the growing concerns. Blockchain allows decentralized identity management, helping users have control of their digital identities without relying on central authority.
Example: IT companies are incorporating blockchain-based authentication systems to offer safe access management. Employees and users can verify their identities by making use of blockchain-powered credentials, decreasing the risk of any unauthorized access and fraud of identity.
Protecting data breaches
Traditional centralized databases are the main targets for hackers, as a single breach can compromise sensitive data. The decentralized nature of Blockchain, substantially decreases this risk, as there are central points of failure.
Example: Healthcare IT systems are making use of blockchain for storage of the patient records safely. As every record is encrypted and stored in various nodes, it stays protected against breaches and cyberattacks.
Verification of data and trustworthiness
Manipulation of data and misinformation are two main problems in IT-driven industries. The transparency in blockchain makes sure that data stays verifiable and trustworthy, facilitating organizations in validating information without depending on third parties.
Example: IT research institutions are making use of blockchain for storing and verifying research findings, making sure that scientific data stays authentic and unchanged over time.
Difficulties in executing blockchain
Despite all the benefits, blockchain adoption in IT supply chains and data integrity face many difficulties.
- Measurability problems: Managing a large volume of transactions usually slows down the blockchain networks.
- Uncertainties in regulation: Governments and regulatory bodies are still required for compliance frameworks for blockchain technology.
- Integration complications: Integration of blockchain with legacy IT systems needs substantial investment and technical expertise.
- Consumption of energy: Some of the blockchain networks, mainly those that use proof of work, consume high resources of energy.
Conclusion
Blockchain is bringing in transformation in IT supply chains and data integrity providing increased transparency, safety and effectiveness. Through the removal of intermediaries, prevention of fraud and making sure there is immutable data storage, Blockchain is addressing important pain points in IT functioning. While difficulties are there, consistent developments in blockchain technology are making the way for a more safe and effective digital ecosystem.
As businesses continue adopting blockchain-driven solutions, the IT industry is all set to experience high levels of trust, safety and effectiveness, thereby bringing in a revolution in how supply chains and data integrity are being managed in this digital age.